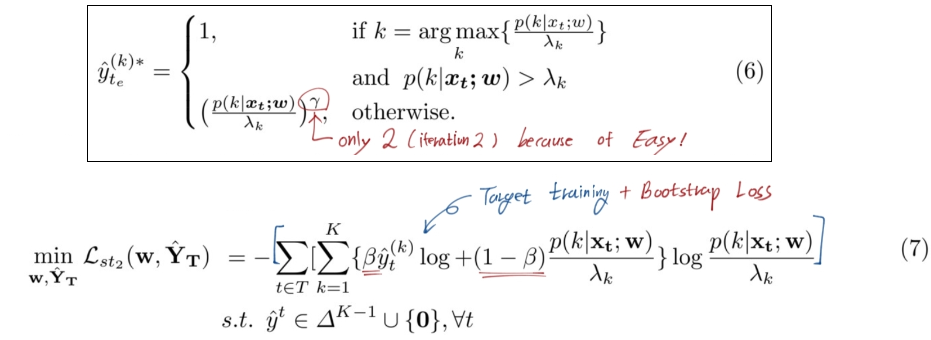【Domain】Two-phase Pseudo Label based Domain Adaptation
- 논문 : Two-phase Pseudo Label Densification for Self-training based Domain Adaptation
분류 : paperswithcode - Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
저자 : Inkyu Shin, Sanghyun Woo, Fei Pan, In So Kweon
읽는 배경 : 현재 Domain adapation, Self-supervise이 연구실의 중심 연구 주제로 많이 사용되고 있다. 판 페이 박사과정 선배가 추천해준 논문을 읽기 전에, 신인규 석사과정 선배님이 작성하신 논문을 먼저 읽는게 좋을 것 같다고 생각했다. 아래의 배울 포인트 때문이다.
- 읽으면서 생각할 포인트 : Reference를 어떻게 추가했나? domain adaptation과 Self-supervised에 대해서 내가 추가적으로 공부해야하는게 뭘까? Abstract가 가장 중요하다고 하는데 선배님은 어떻게 작성하셨나? relative work에 대해서 얼마나 상세하게 이해하셨고 그 흐름을 어떤 식으로 잡고 가셨나? (어떤 의문, 반박으로 다른 모델이 나왔고 등등… 그래서 핵심 모델은 뭐고 과거 흐름은 뭐였는지 등등…) 석사 1년동안 내가 이정도 논문을 쓰기위해서 가져아할 자세는 무엇일까?
- 느낀점
- 현재 나와있는 모델에 대한 의문, 의심, 질문, 반박에서 논문이 시작했다.
- “Make your paper look similar to a typical ML paper.” 을 지키기 위해 아래와 같이 논문의 흐름. the present and problems and issues, ours Solution 으로 나열해가는 흐름에 대해서 잘 기록해 두자. 지금부터 해야한다.
- 역시나 deeplab을 사용하고 그 위에 CRST를 올리고 그 위에 TPLD를 올린방식이다. 따라서 deeplab까지의 계보 즉, recognition의 계보를 최대한 확실히 알아놔야 겠다.
- 질문&답변
- ^yk가 pseudo targer label이라면 이건 어떤 신경망으로 target data를 예측해놓은 결과이지?? w는 아닐테고…
- w로 예측하는거 맞다. 그리고 대신 ^yk값은 Eq.(2)(4) 번 처럼 1 or 0의 값을 가진다. softmax 확률 값이 아니다.
- 이 분야를 항상 관심을 두고 계셨던 건지? 그래서 그 분야의 논문을 항상 읽어오신 건지?
- 논문을 준비하신 기간?
- 코드 제작은 어떻게 하셨는지? 어떤 코드 참고 및 어떤 방식으로 수정? 몇 퍼센트 수정 및 추가? 코드 제작 긱나?
- 석사기간에 이런 좋은 논문을 쓰는게 쉽지 않은데… 혹시 팁이 있으신지?
- ^yk가 pseudo targer label이라면 이건 어떤 신경망으로 target data를 예측해놓은 결과이지?? w는 아닐테고…
- 1선배님조언
- 논문 읽는데 너무 많은 시간을 투자하지 말아라. 핵심만 읽어라
- 최근 논문으로 흐름을 항상 따라라
- 2선배님조언
- AD에서 연결할 수 있는 관심있으신 분야 -> Video, Active learning, Semi-supervise, Labeling down + Performance increment
- Awesome domain adaptation 을 참고해서 괜찮은거 공부해보고, 일부 분야는 발행 논문이 적은데 그 곳을 집중해서 파보는 것도 괜찮다.
- 특히 DA분야는 가짜가 많으니 조심. 정말 모델에 대입 해봤을 때, 성능향상이 이뤄진다면 짜릿.
- 과제!! 현재 과제가 어떤 과제가 있는지 알아보고, 그 과제를 하기 위해서 미리미리 공부해놓고 그 과제를 하고 싶다고 먼저 말해놓는게 좋다. 따라서 몇몇 대화를 해본 선배님들에게 직접 찾아가서 현재 하시는 과제가 무엇인지 무엇을 미리 공부해놓으면 좋은지 알아보기
- 다 읽은 후, 필수로 읽어야 겠다고 생각이 든 논문
- CBST-class-balanced self-training-2018 (class-wise thresholding value λ 가 뭔지 알려줌 [39])
- CRST-Confidence Regularized Self-Training - 2019 [40]
- ADVENT: Adversarial Entropy Minimization for Domain Adaptation - easy vs hard 분별하는 discriminator 왜 사용하는지 적혀 있음 [37]
- Training deep neural networks on noisy labels with bootstrapping (12. 2014) - bootstrapping
- map high-dimensional features to 2D space feature Using t-SNE [27]
- [1] domain adaptation - object detection
- [4] domain adaptation - semantic segmentation
0. Abstract
- the present and problems : The self-training generates target pseudo labels like only the confident predictions(Relative work의 self-training내용 참조). So that this approach produce sparse pseudo labels (희박한/흐릿흐릿한/빈약한 예측 결과) in practice.
- why problem : suboptimal, error-prone model
- Solution : TPLD (Two-phase Pseudo Label Densification) ⭐⭐
- the first phase : Sliding window voting to propagate the confident predictions, Using Image’s intrinsic spatial-correlations.
- the second phase : image-level confidence score -> easy-hard classification.
- easy samples : easy’s full pseudo label. ,while pushing hard to easy.
- hard samples : adversarial learning to enforce hard-to-easy feature alignment.
- additional tech : the bootstrapping mechanism (in order to ease the training process and avoid noisy predictions.)
- result : 다른 self-training 모델에 쉽게 integrated 가능. 최근 self-training framework, CRST에 결합해서 SOTA달성
1. Introduction
- the present models
- Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) 는 labeled source 에서 unlabeled target를 학습하는데 도움이 된다. 이 논문에서는 Semantic segmentation 문제에 대해 UDA를 적용한다.
- UDA 의 핵심적으로 adversarial learning에 근간을 둔다. 이 방법을 통해서 source와 target의 feature distributions을 효과적으로 줄일 수 있다.
- 최근에는 다른 방향으로 self-training 이라는 것이 나왔다. pseudo labels corresponding to high prediction scores(예측 결과를 “가짜 label(annotation)”로 사용한 것)을 이용해서 네트워크를 생성한다. 대표적인 모델이 CBST-2018와 CRST-2019 이다. in multiple UDA.
- [labeled source data] VS [pseudo labeled target data]
- CBST’s key word - self-training loss / domain-invariant ‘features and classifiers’ / class balancing strategy and spatial priors.
- CRST’s key word - the feasible space of pseudo labels / regularizer in loss to prevent overconfident predictions.
- 문제점 : excessively cut-out the predictions.
- 문제로 인한 결과 : sparse pseudo labels.
- 멍청한 해결책 : lowering the selection threshold.
- 우리의 해결책 : ⭐⭐
- Abstract의 Solution에 정리 잘해 둠. 그거 다시 읽기.
- 경험적으로, Easy sample(label 예측을 confident자신있게 판단한 이미지)은 ground-true에 가까웠다. 따라서 easy sample’s full pseudo labels(GT은 아니만 그래도 GT와 가까운 예측값=가짜 라벨값)을 사용하기로 했다. 반대로 hard sample에 대해서는 (hard-easy adaption의) adversarial loss를 사용했다.
- the bootstrapping mechanism 사용
- Summarize our contributions
- 이것을 사용한 첫번째 사례이다. / TPLD 요약 / 새로운 loss bootstrapping mech. / ablation studies
2. Related works
- Domain Adaptation
- 목적 : the performance drop by the distribution mismatch
- 계보 : adversarial learning -> minimize the discrepancy between source and target feature -> unsupervised domain adaptation. -> 아래 처럼 3개로 분류 가능.
- input-level alignment [5, 17, 28, 34]
- intermediate feature-level alignment [18, 19, 23, 25, 37]
- output-level alignment [36]
- 하지만 위 방법들은 taget domain signal을 충분히 이용하지 못한다.
- 그래서 self-training based UDA approaches [CBST, CRST]이 나와서, 성능에서 우의를 차지하고 있다.
- Self-training
- 장점 : 위의 문제점 해결. Explore the supervision signals from the target domain.
- 간단 메카니즘 :
- Use prediction target data from the source-trained model (= pseudo-labels).
- Re-train the current model in the target domain. (pseudo-labels를 GT로 설정하여)
- CBST, CRST도 있지만, 우리는 sparse pseudo label 문제에 집중했다. introduction정리와 동일.
3. Preliminaries
- source domain : (xs, ys)
- target domain : (xt)
- we train the network to infer pseudo target label.
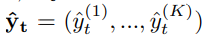 여기서 K는 the total number of classes.
여기서 K는 the total number of classes. 
- (2):
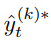 =
=  Pseudo Label은 가짜이지만 ‘정답’값(GT값)이므로 0 or 1 의 값을 가져야 한다.
Pseudo Label은 가짜이지만 ‘정답’값(GT값)이므로 0 or 1 의 값을 가져야 한다.
Noisy label handling
- Training deep neural networks on noisy labels with bootstrapping (12. 2014)
- bootstrapping loss = (-붙어야 함. 아래 수식에 붙음)
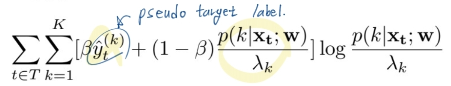
- beta는 그냥 trade-off의 벨런스 조정 값이다. 어떤 값에 집중하게 만들 것 인가.
- 직관적으로 w모델이 pseudo target label을 더 잘 예측하게 만들고, 그 예측값에 더 confident하게 만든다.
4. Method
- phase1을 충분히 학습시키고, phase2를 더 학습시켰다. 모든 phase에서 bootstrapping 방법을 사용하였다.

4.1 : 1st phase : Voting based Densification
- 문제점 : (2)의 수식에서 보듯이, class에 따른 possibility값이 큰 class에 대해, λ_k이상의 값을 가져아 pseudo label값이 주어진다. 여기서 sparse pseudo labels 문제가 발생한다.
- 해결책 : Sliding window-based voting. 주변 픽셀은 (픽셀, 예측)값이 비슷할 수 있다는 사실을 이용.
- the neighboring confident prediction values. 아래에서 x3은 iteration.
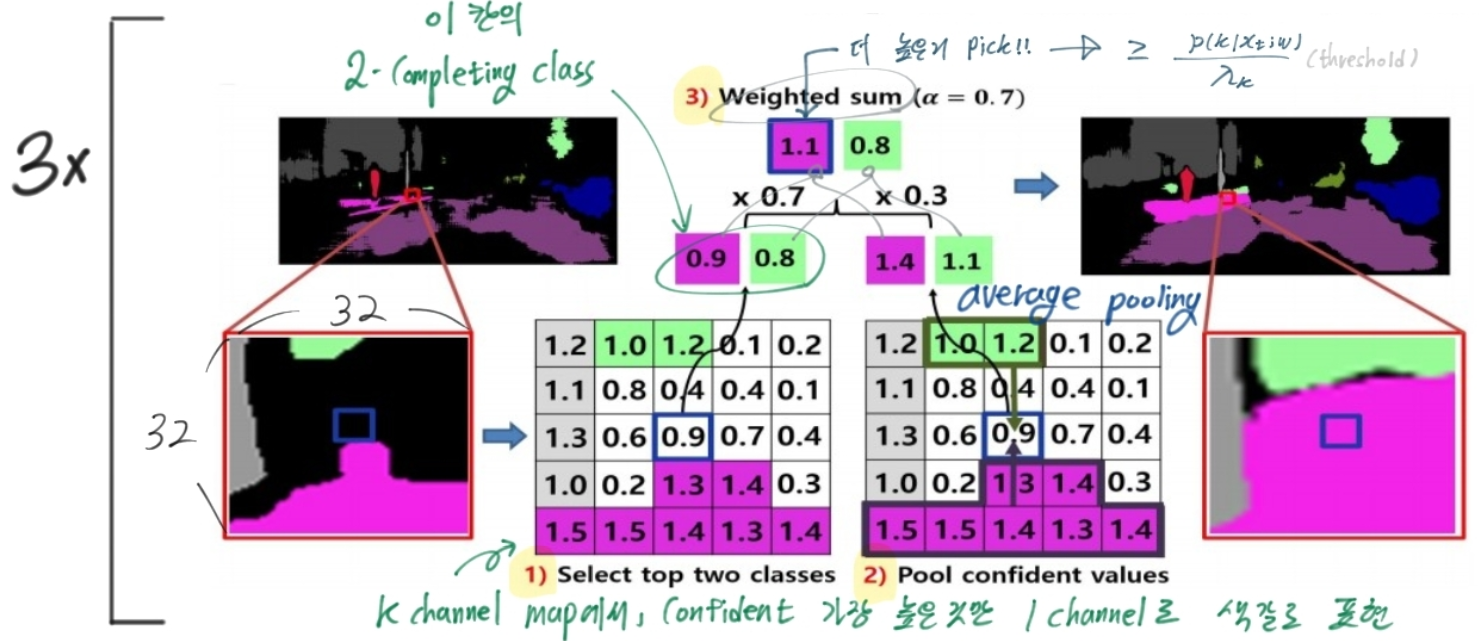
- Loss 함수 교체
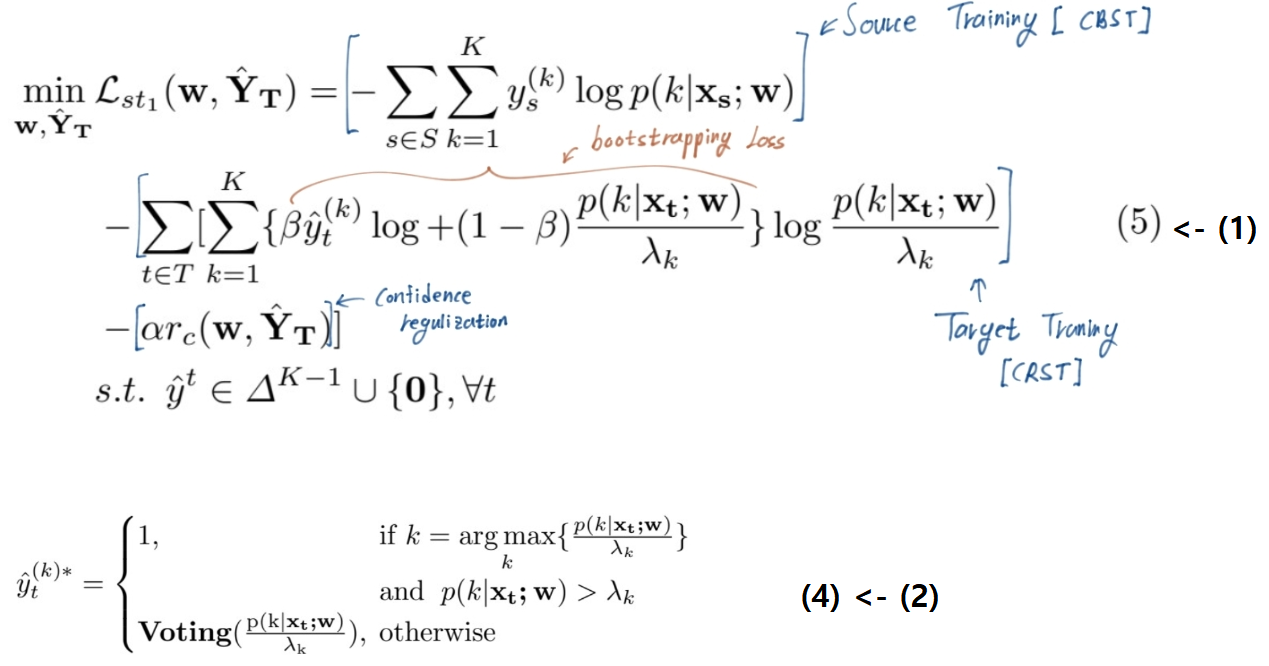
4.2 : 2nd phase: Easy-Hard Classification based Densification
위와 같은 voting 작업을 한다 할지라도, fully densified pseudo labels을 만들수가 없다. local window이기 때문이다. 따라서 full-pseudo label training을 위해서 다른 방법을 제시하였다.
target sample을 hard와 easy로 나누는 방법
- 한장의 이미지를 예측하면 w x h x K 의 prediction possibility 값이 나올거다. 그것에 대해서,
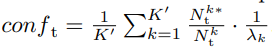
- Nk_t는 k-class를 가지는 pixel의 전체 수
- Nk_t*는 Nk_t 중에서 λ_k(class-wise thresholding value[39]) 이상의 픽셀 수
- 위의 2개를 나누면, k클래스에 대해서 모델이 자신있게 predict를 하는 비율을 의미한다.
- 이미지 한장이 가지는 conf값이 충분히(q 보다) 크면, 이 target 이미지를 자신있게 예측했어! 라는 의미로 이 이미지는 easy Image라고 정의한다.
- 이미지 한장이 가지는 conf값이 q 보다 작으면, 이 target 이미지를 자신없게 예측했어ㅠ 라는 의미로 이 이미지는 hard Image라고 정의한다.
- λ_k(1이하)로 한번 나눠준 이유는, 너무 많은 easy가 나오지 않도록 만든다. 예측하기 아주 쉬운 이미지에 대해서.
- 실험을 통해서 q를 0.3으로 설정하는 것이 가장 좋은 mIOU를 가져다 주는 것으로 판단할 수 있었다.
이미지를 easy, hard로 나누고, 각각에 대해 다른 Loss 함수를 적용했다.
easy : full pseudo label predictions + bootstrapping loss
hard : adversarial learning to push hard examples to be like easy samples
- In order to align the feature from hard to easy, discriminator D_intra를 학습시킨다. 이 discriminator는 이 이미지가 hard이미지인지 easy이미지 인지 판단하는 discriminator이다.
- 이 내용을 완벽하게 이해하려면 [37] 을 이해해야한다. 위의 식은 easy면 1. hard만 0.로 판단하는 discriminator를 만들기 위한 loss값이고, 아래는 hard를 1이라고 판단하게 만드는 discriminator loss이다.
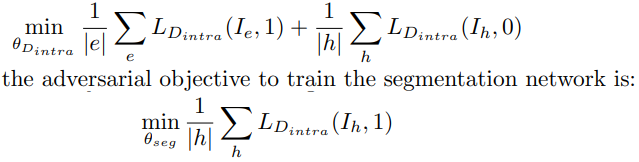
5. Experiments
- GTA5 [31] to Cityscapes [6]
- SYNTHIA [32] to Cityscapes
- 5.2 - Implementation details (backbone모델(VGG16), segmentation model(deeplab))
- 5.3 - Main Results (with Figure)
- 5.4 - Ablation study, 5.5 - Parameter analysis
- conf에서 1/λ의 역할
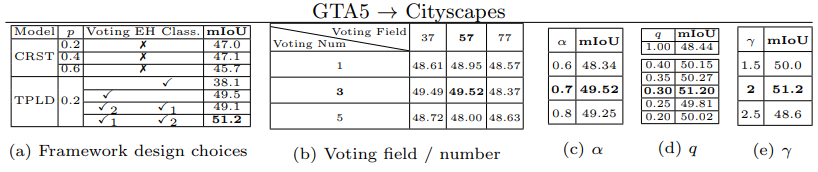
- 5.6 Loss function analysis
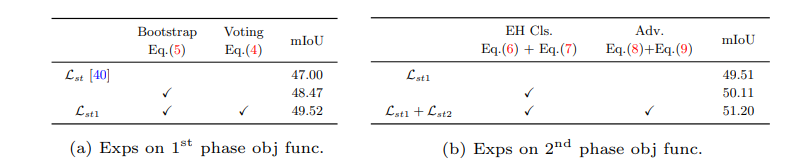
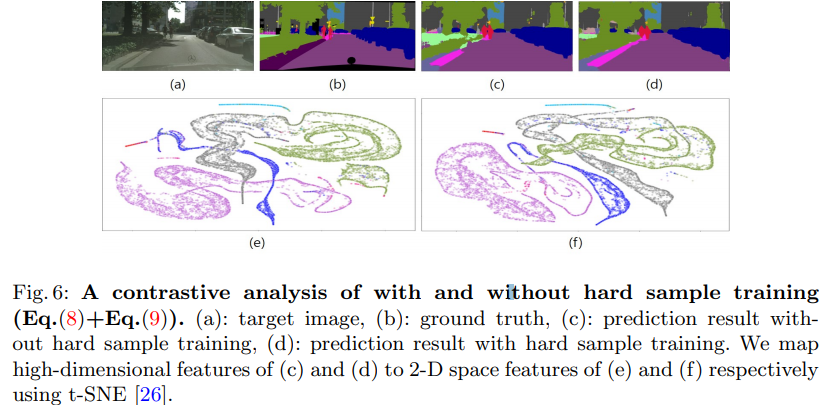
- Especially for the hard sample training, we conduct a contrastive analysis in Fig. 6. (이 FIg 6 그림을 이해하기 위해서는 논문 [26]을 꼭 일어야 겠다.)
- We map high-dimensional features of (c) and (d) to 2-D space features of (e) and (f) respectively using t-SNE [26]

6. Conclusions
- Unsuperivsed Domain Adaptation에서 좋은 성능을 내었다.