【Self-Supervise】 Self-Supervised-Learning Basics
Self-Supervised-Learning Basics
Self-Supervised-Learning Basics on webs
- 데이터의 사람이 만든 ‘annotation Label’이 없어도, Feature Extractor(Pre-trained Model)을 만들 수 있는 몇가지 방법들에 대해 기초만 알아보자.
0. reference
- https://project.inria.fr/paiss/files/2018/07/zisserman-self-supervised.pdf
- https://lilianweng.github.io/lil-log/2019/11/10/self-supervised-learning.html
- https://www.fast.ai/2020/01/13/self_supervised/
1. zisserman-self-supervised - 2018.07
- 모델에 대한 상세한 설명은 없다. 하지만 전체적은 윤각선을 만들기 위해 먼저 빠르게 보기로 했다.
- Supervise-learning : With a large-scale dataset labelled / Can Specify a training loss / Easy to Train the network
- why self-supervision : high Expense of dataset / supervision-starved / vast numbers of unlabelled images/videos
- how infants may learn : The Development of Embodied Cognition
What is Self-Supervision?
- Self-Supervision을 통해서 Feature Extrator를 생성하고, 그렇게 얻은 (self를 해서 얻은) FeatureExtractor를 가지고, 적은 데이터 만을 가지고 (supervision 처럼) Classifier를 학습시키기 위함.
- Three parts
- From Images
- From videos
- From videos with sound
2.Part (1) - Images

- (2014) relative positioning : Origin Image만으로도 학습이 가능하다. 이걸로 Pretrained를 시키고 나중에 supervise로 refine 학습을 진행한다.
- (2014) colourization
- (2014) exemplar networks : Perturb/distort image crops, Train to classify as same class
- 학습 절차
- backbone에 self-supervised training을 먼저 수행한다. using 위의 다양한 방법들.
- backbone freeze!
- 그리고 train classifier.
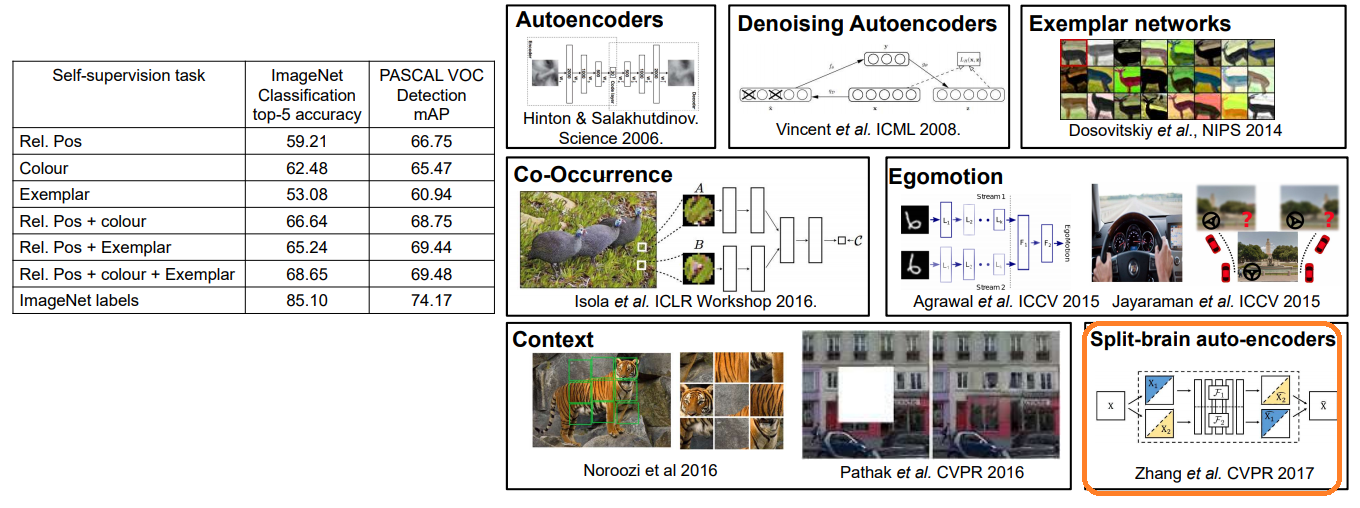
- 아래와 같이 supervised를 사용한 것 보다는 낮은 성능이지만, 그래도 성능이 좋아지고 있다. 그리고 아래 오른쪽에 새로운 Self-Supervised 방법들을 그림으로 추가해 놓았다. (참고만 하자)
- (2018) Image Transformation : Unsupervised representation learning by predicting image rotations
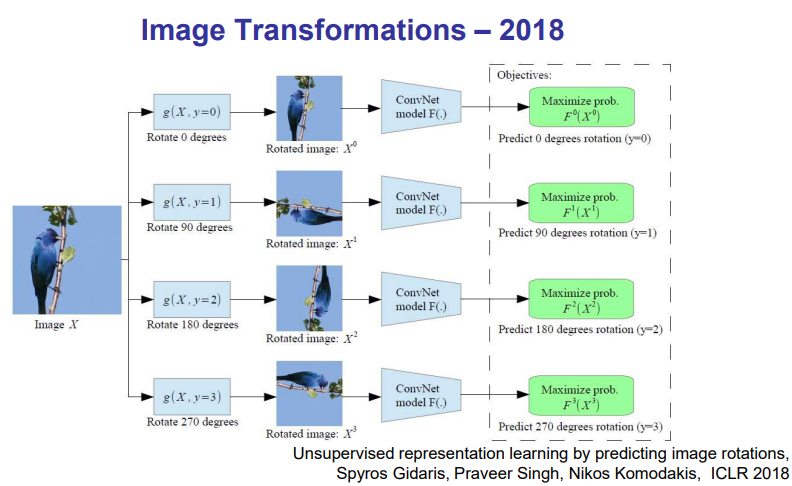
- Rotaion으로 학습한 AlexNet Architecture 모델에서 좋은 성능이 나왔다. then Relative Position, Colourization.
2.Part (2) - Videos
- Video의 어떤 정보를 이용해서 Self-Supervised할 수 있을까?
- Temporal order of the frames => 1. Video sequence orde
- Nearby (in time) frames => 2. Video direction
- Motion of objects => 3. Video tracking
1. Video sequence order 를 이용하는 방법
- 예를 들어, 3개의 동영상 frame이 있다고 가정했을 때, frames order [1 -> 2 -> 3]를 예측하게 하는 방법
- (a) Shuffle and Learn
- Using ‘high motion window‘(동영상 중에서도 핵심적인 Action 부분 3장) of Dataset (Action Reognition) that is imformative(유용한) training tutples
- Input : 이미지 튜플(3장의 프레임) -> Return : 각 프레임의 순서 예측
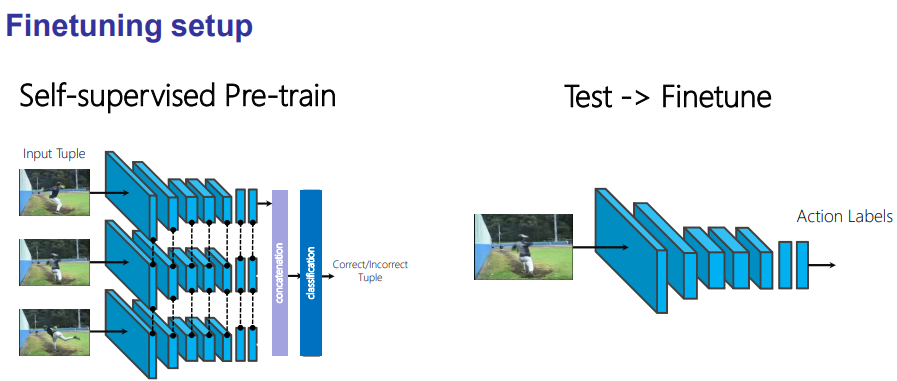
- 위와 같이, Sequence order를 이용해서 학습시킨다. 3개의 모델은 파라메터를 공유한다. 이 모델을 사용해 [Action Label 예측 모델’/’Human Pose Estimation] 데이터셋을 이용해 fine-tuning한다.
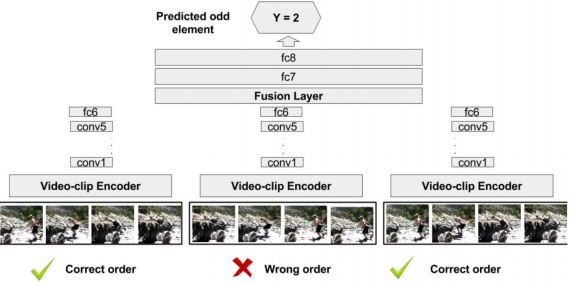
- (b) Odd-One-Out Networks
- Summary
- Important to select informative data in training : 중요한 정보를 선택해서 그것으로 학습을 시켜야 한다. 예를 들어 회전, 동영상 순서 등은 data에서 매우 중요한 정보라고 할 수 있다.
- 직접적으로 의도하지는 않았지만, (a) shuffle and learn 과정을 통해서 모델은 ‘Human Pose Estimation’ 문제에서 필요한 feature extractor를 만들어 냈을 것 이다
2. Video direction(방향) 를 이용하는 방법
- video playing forwards or backwards, 정방향 재생중인가? 뒤로 거꾸로 재생중인가?
- gravity, entropy, friction, causality 와 같은 물리적 법칙들에 대한 feature extractor를 생성할 것이다.
- (a) T-CAM Model
- Input: optical flow in two chunks(10 frame 동영상 뭉치)
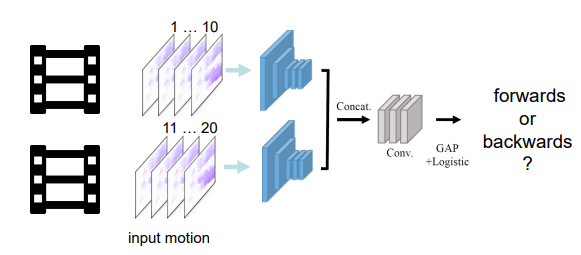
- 동영상 전체에서, 핵심 장면을 이용한다.
- 위의 pre-train network를 이용해서, Fine tune & test 한다. UCF101 (human action classification) 데이터를 사용해서. 그래서 Network는 the best performance ever를 얻었다.
3. Video tracking 를 이용하는 방법
- (a) Tracking Emerges by Colorizing Videos (2018)

- color 와 object tracking에는 분명한 관계가 있다!! 위의 그림처럼 같은 색을 tracking 한다면, Tracing 과제에서 절반이상은 성공이다.
- Input : reference Frame (Color 존재), Input Frame(monochrome 흑백)
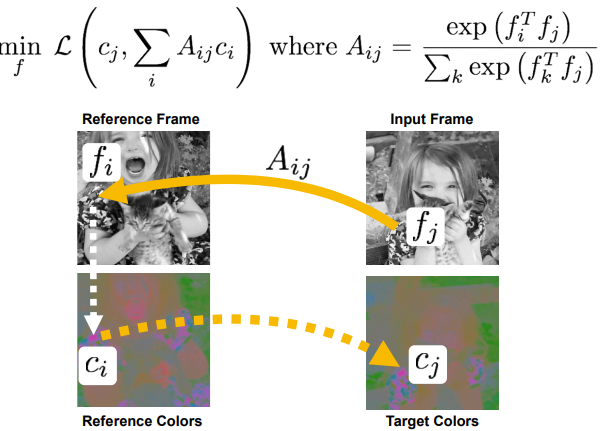
- A는 공간유사도(내적은 두 백터가 유사할 수록 큰 값이 나오므로.)
- C_i는 참고하는 부분의 color
- ∑Ac는 참고 공간(f_i)을 전체 훓어 봤을때, 가장 적절한 공간(f_j)의 색깔이 (다른 공간 색과 적절히 융합(∑)되어) 계산되어 나오겠다. 정답값인 C_j와 비교해서 loss 도출.

- 괜찮은 colorization 성능 도출 되었다.
- 이렇게 학습시킨 모델을 사용해서, 아래의 문제에서도 좋은 결과를 얻을 수 있었다. 아래의 문제에서 Reference Frame은 각각 previous frame’s Instance color, previous frame’s pose은 항상 제공된다.

- (a) Tracking Emerges by Colorizing Videos (2018)
2.Part (3) - Videos with Sound
- Key : Sound and Frames are Semantically consistent and Synchronized. (일관적인 관계가 있다.)
- Objective(목적): use vision and sound to learn from each other (서로서로를 예측하기 위해 서로를 사용한다.)
- (a) Audio-Visual Embedding (AVE-Net)

- output : Positive or Negative.
- Results Audio features extracor들을 Sound Classification (ESC-50 dataset) 에서 사용하면 아주 좋은 성능을 얻어냄.
- Results Visual features extracor들을 ImageNet images에서 사용해서도 좋은 성능을 얻는다.
- (b) AVOL-Net
- 사진의 어디서 소리가 나는지 예측하는 모델. 아래의 그림만으로 이해가 한정적이니, 논문 보기.
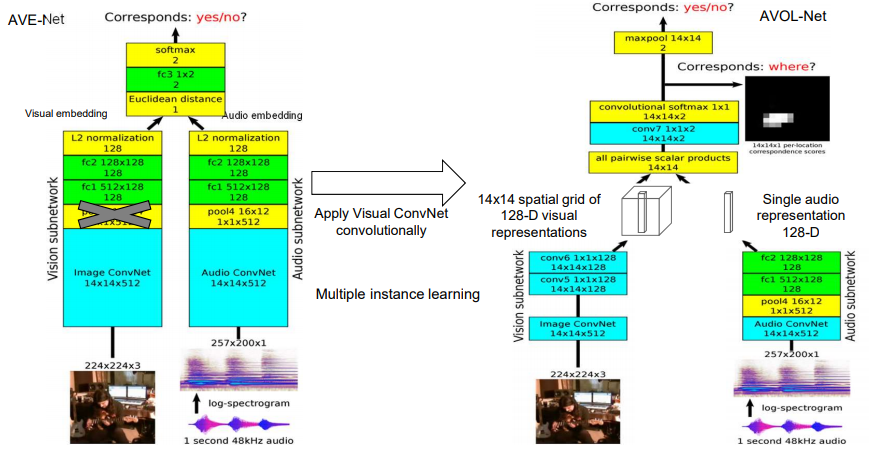
- input: audio and video frame
- Output: localization heatmap on frame
- Other papers.. : (c) Ambient sound provides supervision for visual learning / Visually indicated sounds
- DataSet : AudioSet from Youtube
- 지금까지 소리와 이미지의 상관성(correspondence)를 파악하고자 노력했다. 이제는 이미지와 소리와의 synchronization을 파악하는 노력을 해보자.
- 우리는 입모양으로 그 사람이 뭐라고 말하는지 유추가 가능하다. 시각장애인들은 더더욱.

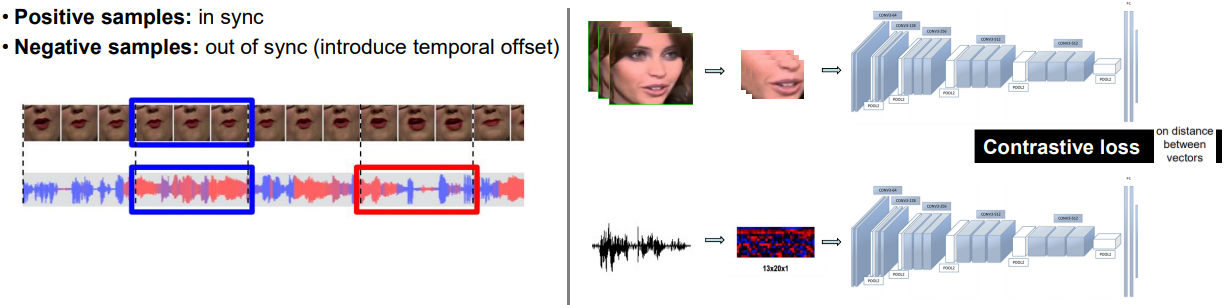
- 위와 같은 방식으로 모델을 학습시킨다. 그렇게 얻은 모델을 가지고 Lip Synchronization, Active speaker detection의 과제를 수행했을때 좋은 성능을 얻을 수 있었다.
2.3 - Summary
- Self-supervised learning from images/video
- without explicit supervision, 학습이 가능하다. (Pre-train모델을 만들 수 있었다.)
- we can Learn visual representations = 적절한 Visual Feature Extractor들을 뽑을 수 있었다.
- Self-Supervised Learning from videos with sound
- Intra- and cross-modal retrieval(회복) - 서로의 데이터를 가지고, 상호 학습이 가능했다.
- Learn to localize sounds (어디서 소리가 나는지 예측하는 모델)
- 영상+소리를 pair로 사용하는 것처럼, 다른 domain pair에는 무엇이 있을까??
- face(not lip) - voice
- Infrared(적외선) - visible
- RGB - Depth
- Stereo streams - visible