【Self】Self-training with Noisy Student improves ImageNet classification
- 논문 : Self-training with Noisy Student improves ImageNet classification
- 분류 : classification (Detection)
- 저자 : Qizhe Xie, Minh-Thang Luong, Eduard Hovy
- 느낀점
- 목차
- Paper Review
- Noise 기법 정리
Self-training with Noisy Student
1. Conclusion, Abstract
- 과거의 기법들이, ImageNet에서의 성능 향상을 위해서, 수십억장의 web-scale extra labeled images와 같은 많은
weakly labeled Instagram images이 필요한weakly-supervised learning을 수행했었다. - 하지만 우리는
unlabeled images을 사용함으로써, 상당한 성능향상을 얻어내었다. 즉 the student에게 Nosie를 추가해 줌으로써, 성능향상을 이루는,self-training = Noisy Student Training = semi-supervised learning기법을 사용하였다. - EfficientNet에 Noisy Student Training를 적용함으로써 accuracy improvement와 robustness boost를 획득했다.
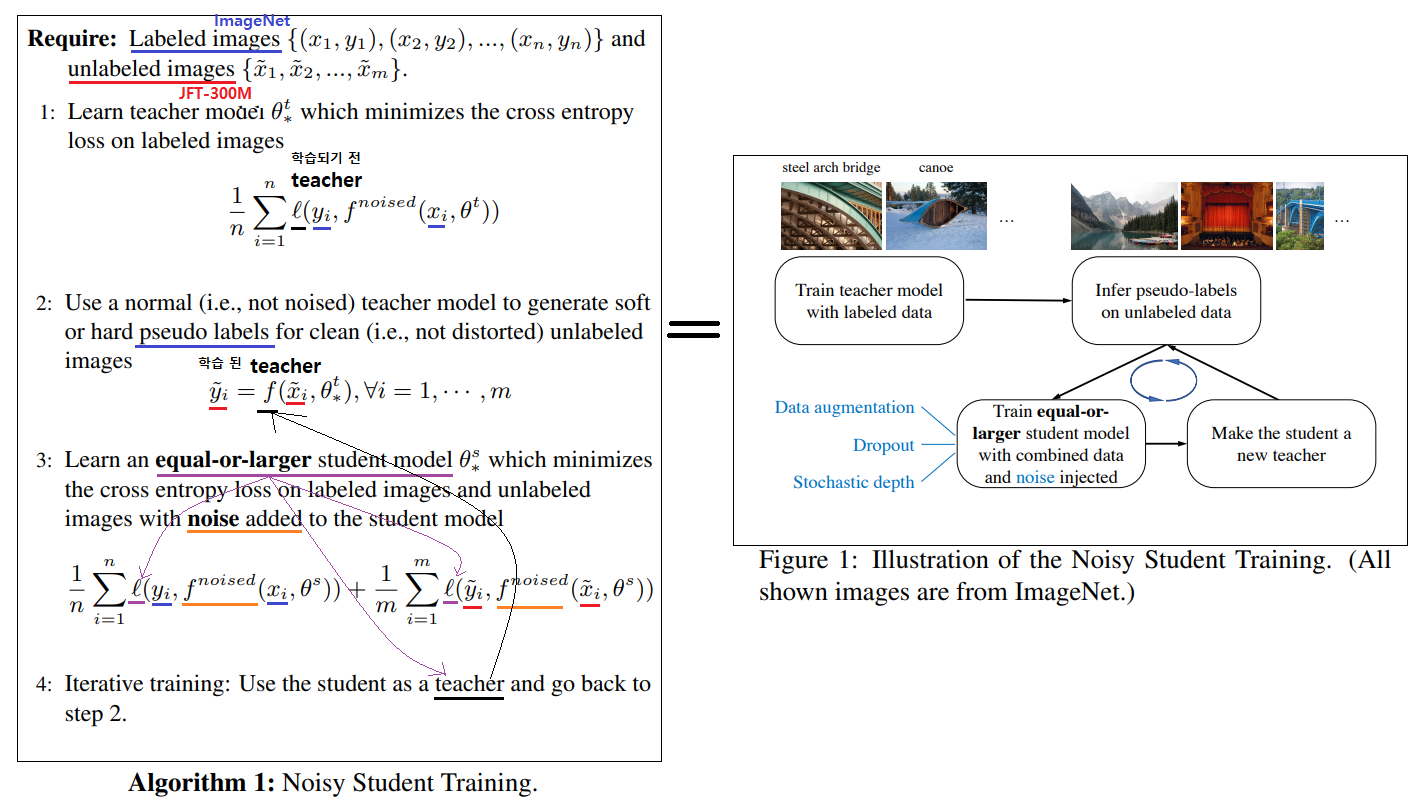
- 전체 과정은 다음과 같다. (아래 그림과 함께 참조)
- 우선 Labeled Image를 가지고 EfficientNet Model(E)을 학습시킨다.
- E를 Teacher로 사용하여, 가지고 300M개의 unlabeled images에 대해서, Pseudo labels를 생성한다. (
self-training을 하고 있다고 볼 수 있고, Soft (a continuous distribution) or Hard (a one-hot distribution) 둘 다 될 수 있다.) - larger EfficientNet를 student model로 간주하고, labeld + sseudo labeld images를 사용해 학습시킨다.
- student의 학습을 진행하는 동안, dropout[76], stochastic depth[37], RandAugment data augmentation[18] 와 같은 noise를 주입한다.
- teacher보다 더 똑똑한 student가 탄생한다!
2. Noisy Student Training
[ 참고 블로그 내용 정리 ]
- Knowledge Distillation 기법과 차이점을 다시 고려해보면, Knowledge Distillation에서는 Teacher보다 작은 Size(complexity)의 Student Model을 학습시킨다. 그리고 Student에서도 Labeled dataset만 사용해 학습시킨다.
- Fix train-test resolution discrepancy 기법 : 이 기법은 먼저 첫 350 epoch 동안에는 이미지를 작은 resolution으로 학습시킨다. 그리고 1.5 epoch 동안, 큰 resolution을 가지는 unaugmented labeled images 를 가지고 학습시키며 fine-tuning을 진행한다. (이 방법을 제안한 논문과 마찬가지로) fine-tuning하는 동안에 shallow layer(input에 가까운 Layer)는 freeze하여 학습시켰다고 한다.
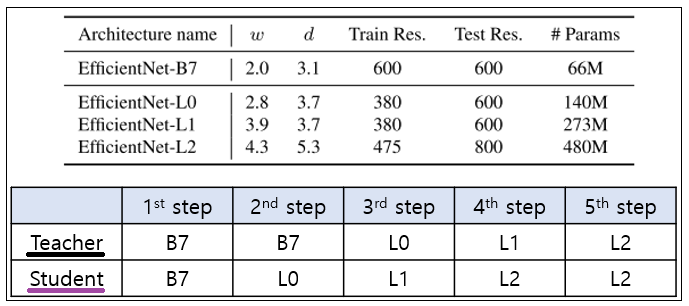
- Iterative Training : 위의 알고리즘을 한단어로 표현하면, 반복학습(iterative training)이라고 할 수 있다. 처음에 EfficientNet-B7을 Teacher로 사용하고, 더 큰 모델의 student 모델이 L0, L1, L2가 된다. 그 전체 과정과 모델의 [파라메터 수, width, depth, resolution]는 아래와 같다.
- 결과
- Noisy Student (L2)은 SOTA를 달성했고, 기존 SOTA보다 적은 Parameter를 보유한다. 그리고 Extra Data가 label이 아닌 unlabel이며 그 크기도 적다.
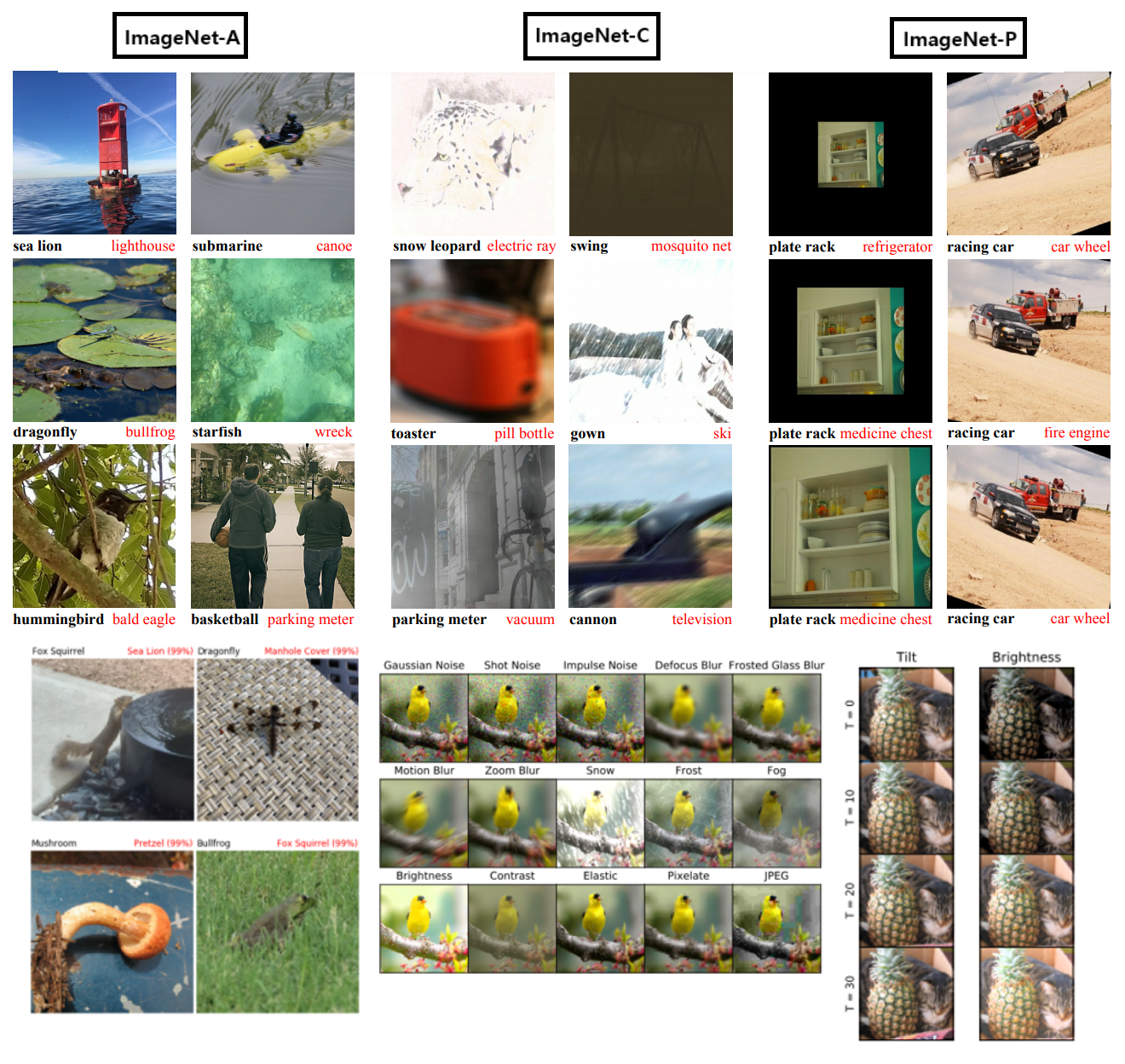
- 모델의 신빙성과 Robustness를 측정하기 위해 Dan Hendrycks에 의해 제안된, ImageNet-C, ImageNet-P(blurring, fogging, rotation, scaling과 같은 대표적인 Corruption과 Perturbation 이용), ImageNet-A(Natural Image=자연 그 상태에서 찍은 사진. 단색 배경이나, 큰 객체가 아니라) 데이터 셋이 있다.
- 위와 같은 Robustness 테스트에서도 좋은 성능을 보여주고 있고, Adversarial Attack에 대해서 얼마나 강건한지에 대한 실험 그래프(Figure 3)를 보더라도 좋은 robustness를 가지는 것을 확인할 수 있다. Noise에 학습된 데이터라서 그런지 확실히 EfficientNet보다 좋은 robustness를 보인다.
- Noisy Student Training
- self-training 의 향상된 버전이라고 할 수 있다.
- (noise를 사용하지 않고, Smaller student를 만드는) Knowledge Distillation 과는 다르다. 우리의 방법은 Knowledge Expansion이라고 할 수 있다.
- Pseudo code의 Algorithm 위의 이미지에서 참고
- Noising Student (명석한 분석)
- input noise로써 RandAugment를 사용했고, model noise로써 dropout [76] and stochastic depth [37] 을 사용했다. 이런 noise를 통해서, stduent가 Invariances, robustness, consistency 를 획득하게 된다. (특히 Adversarial Attack에 대해서도)
- (First) data augmentation : teacher은 clean image를 보고 high-quality pseudo label을 생성할 때, Student는 augmented image를 봐야한다. 이를 통해서 student 모델은 비교적 정확한 label을 기준으로, consistency를 가질 수 있게 된다.
- (Second) dropout & stochastic depth : teacher은 ensemble 처럼 행동한다. student는 single model 처럼 행동한다. student는 powerful ensemble model을 모방하는 꼴이라고 할 수 있다.
- Other Techniques
- data filtering : 초반에 (지금까지 봐온 (labeled) 이미지와는 조금 많이 다른) out-of-domain image 때문에 teacher모델에서도 low confidence를 가지는 image를 필터링 한다. (나중에 차차 학습한다.)
- balancing : labeled images에서 class에 따른 이미지 수와, unlabeled images에서 class에 따른 이미지 수를 맞춘다. (내 생각으로, labeled image에 별로 업는 class가 unlabeld image에 많으면 teacher의 pseudo label 자체가 불안정하기 때문에. 이러한 작업을 수행해준다.)
- soft or hard pseudo labels : out-of-domain unlabeled data 에 대해서 soft pseudo label이 좀 더 student 모델에게 도움이 되는 것을 경험적으로 확인했다. (예를들어, confident가 충분히 높지 않으면 soft pseudo labels를 사용하여 student 모델을 학습시키는 방식. )
- Comparisons with Existing SSL(self-supervised learning) Methods
- SSL은 특정한 teacher 모델이 없다. 그냥 자기 자신이 teacher이자 student일 뿐이다. 이전의 모델(teacher)이 low accuracy and high entropy를 가졌다면, 새로운 모델(student) 또한 (Noise 까지 받으며) high entropy predictions 을 하게 만들 뿐이다.
3. Experiments
3.1Experiment Details
- Labeled dataset : ImageNet, 2012 ILSVRC
- Unlabeled dataset : JFT dataset (300M images) public dataset YFCC100M
- data filtering and balancing
- confidence of the label higher than 0.3. 각 클래스에 대해서, 그 중에서 높은 confidence를 가지는 130K 이미지를 선택. 만약 130K 개가 안되면 이미지 복제를 해서라도 130K 맞추기
- 최종적으로 each class can have 130K images 를 가지도록 만든다. (ImageNet 또한 class마다 비슷한 수의 이미지를 가지고 있다고 함)
- Architecture
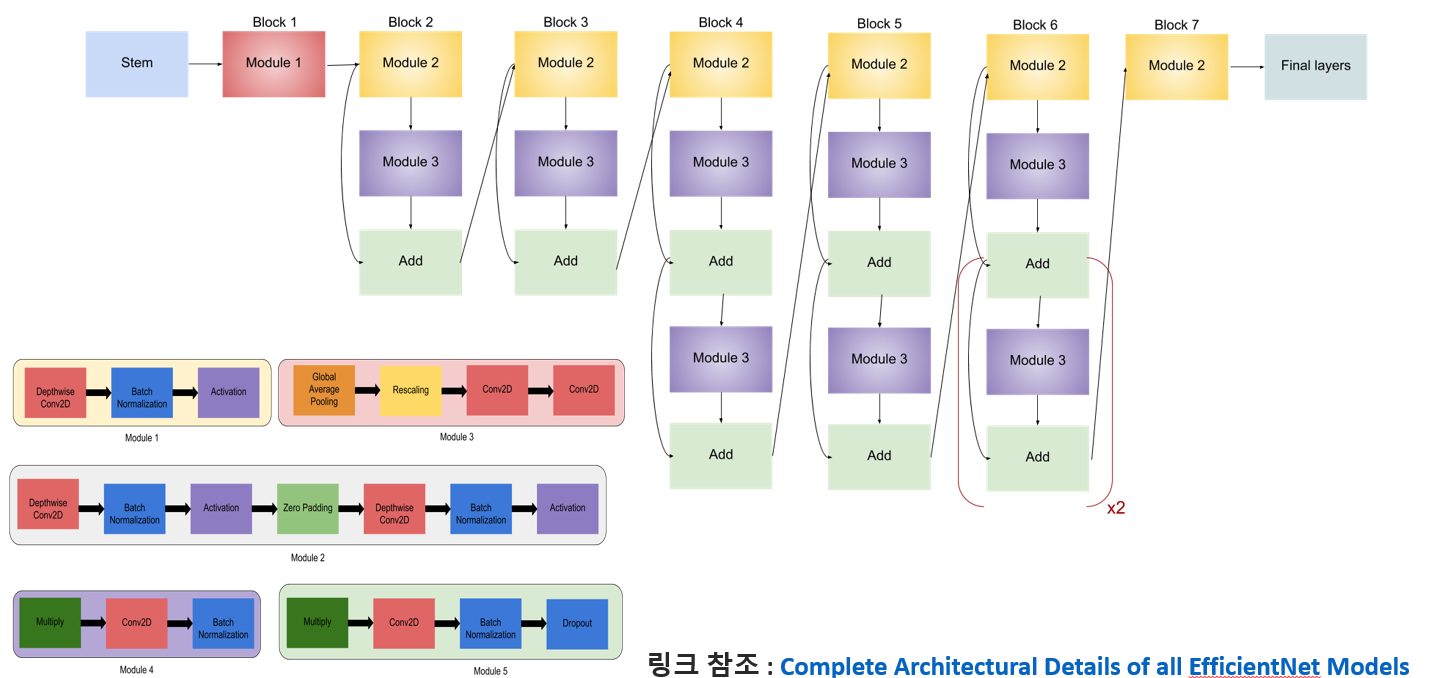
- EfficientNet-B7에서 wider, deeper, lower resolution을 가지는 Network를 만들어서 최종적으로 EfficientNet-B7를 만들었다고 함.
- 아래는 EfficientNet-B0 인데, 여기서 Block을 더 넣는 방식으로 더 깊게 만들고, channel을 인위적으로 늘린다.
- 특히, lower resolution을 사용하는 이유는 2가지인데, (1) 파라메터 수를 너무 과다하지 않게 만들기 위해서 (2) 아래의 ` fix train-test resolution discrepancy` 기법을 사용하기 때문에
- Training details
- epochs : EfficientNet-B4보다 작은 모델은 350. EfficientNet-B4 보다 큰 모델은 700.
- learning rate : labeled batch size 2048 를 학습시킬때, 0.128 로 시작하고, 위의 모델에 대해서 각각 2.4 epochs, 4.8 epochs마다 0.97씩 감소시켰다.
- large batch size for unlabeled images : make full use of large quantities of unlabeled images.
- 6 days on a Cloud TPU v3 Pod, which has 2048 cores, if the unlabeled batch size is 14x the labeled batch size
fix train-test resolution discrepancy기법 [86] : 작은 해상도로 350 epochs 학습시키고, 마지막에 1.5 epochs만 larger resolution unaugmented labeled images 이미지로 학습시킴
- Noise
- the survival probability in stochastic depth : 가장 마지막 residual layer에 대해서 0.8 를 가지고, 초반 layer로 갈수록 점점 증가시킨다.
- dropout rate : 가장 마지막 layer에 대해서 0.5 를 적용하고, 초반 layer로 갈수록 점점 증가시킨다.
- RandAugment : 27 magnitiude
4. Details of Robustness Benchmarks
- ImageNet-A
- 200 classes를 가지는 데이터셋
- the original ImageNet classes are available online. (자연 그대로 상태의 이미지)
- ImageNet-C
- mCE (mean corruption error) : the weighted average of error rate on different corruptions
- Corruptions in ImageNet-C: Gaussian Noise, Shot Noise, Impulse Noise, Defocus Blur, Frosted Glass Blur, Motion Blur, Zoom Blur, Snow, Frost, Fog, Brightness, Contrast, Elastic, Pixelate, JPEG.
- ImageNet-P
- mFR (mean flip rate) : the weighted average of flip probability on different perturbations
- Gaussian Noise, Shot Noise, Motion Blur, Zoom Blur, Snow, Brightness, Translate, Rotate, Tilt, Scale
- RandAugment transformations
- AutoContrast, Equalize, Invert, Rotate, Posterize, Solarize, Color, Contrast, Brightness, Sharpness, ShearX, ShearY, TranslateX and TranslateY.
3.2 ImageNet Results
- ImageNet-C의 평가에 사용된 mCE 지표와 ImageNet-P의 평가에 사용된 mFR 지표는 낮을수록 좋은 값이다.
- 성능지표 표는 첨부하지 않겠다. 쨋든 다 성능이 향상한다.
Noise 기법 정리
- Dropout [2014]
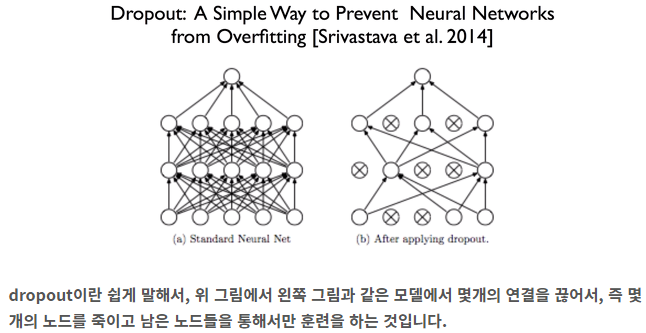
- overfitting 방지
- hidden unit을 일정 확률로 0으로 만드는 regularization 기법이다.
- 후속 연구로, connection(weight)를 끊어버리는 (unit은 다음층 다른 unit과 모두 연결되어 있는데, 이 중 일부만 끊어 버리는 것이다. dropout 보다는 조금 더 작은 regularization(규제)라고 할 수 있다. )
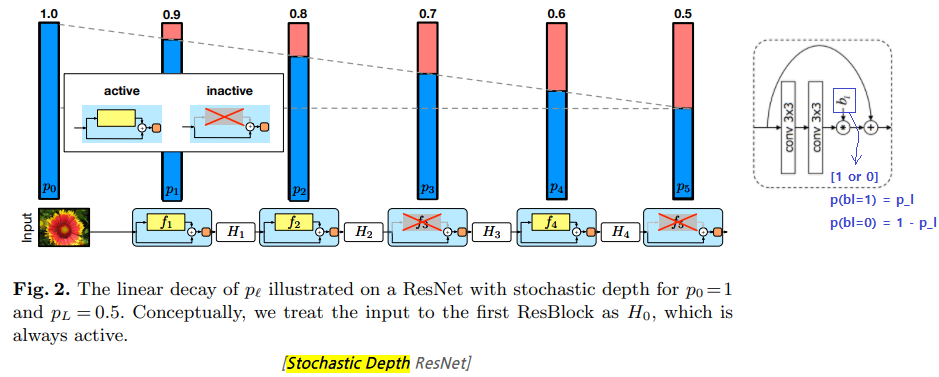
- stochastic depth [2016]
- ResNet의 layer 개수를 overfitting 없이 크게 늘릴 수 있는 방법이다. ResNet1202 를 사용해도 정확도가 오히려 떨어지는 것을 막은 방법이다.
- ResNet에 있어서 훈련할 때에 residual 모듈 내부를 랜덤하게 drop(제거)하는 모델이다. (모듈 내부가 제거되면 residual(=shortcut)만 수행되며, 그냥 모듈 이전의 Feature가 그대로 전달되는 효과가 발생한다.)
- Test시에는 모든 block을 active하게 만든 full-length network를 사용한다.
- p_l = 1 - l/2L
- residual 모듈이 drop하지 않고 살아남을 확률이다.
- L개의 residual 모듈에서 l번째 모듈을 의미한다.
- input에 멀어질 수록, l은 커지고, p_l은 작아진다. 즉 drop 될 확률이 커진다.
- p_l의 확률값에 의해서 b_l (0 or 1 = drop_active or Non_active)이 결정된다.
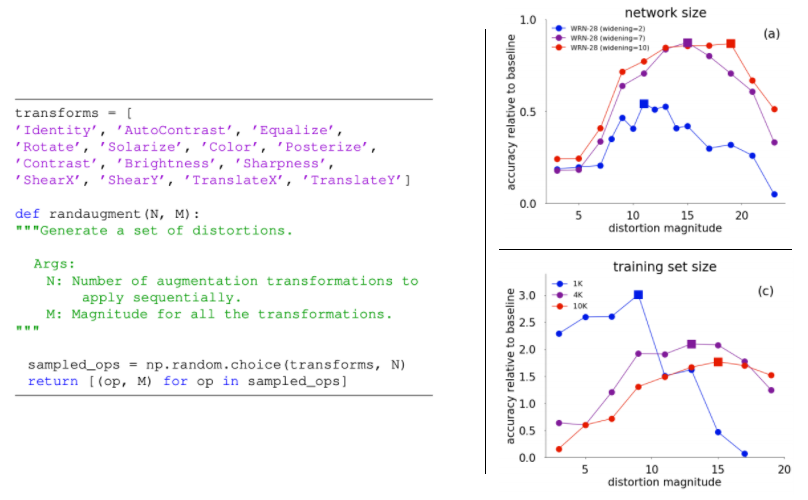
- RandAugment data augmentation [2019]
- 간략하게 말하면, 기존에 다양한 Data Augmentation을 싹 정리해놓은 기법이다.
- 아래와 같은 14가지 Augmetation 기법들을 모아놓고, 랜덤하게 N개를 뽑고, 얼마나 강하게 Transformation(distortion magnitude)를 줄 것인지 M (Magnitude)를 정해준다. (아래 왼쪽의 수도코드 참조)
- 그렇다면 M을 얼마나 주어야 할까? (1) 매번 랜덤하게 주는 방법 (2) 학습이 진행될수록 키우는 방법 (3) 처음부터 끝까지 상수로 놔두는 방법 (4) 상한값 이내에서 랜덤하게 뽑되, 상한가를 점점 높히는 방법
- 모두 실험해본 결과! 모두 같은 성능을 보였다. 따라서 가장 연산 효율이 좋은 (3)번을 사용하기로 했고, 상수 값 M을 몇으로 하는게 가장 좋은 성능을 내는지 실험해 보았다. (아래 오른쪽 그래프 참조) 그래프 분석에 따르면, 최적의 M은 10~15 정도인 것을 알 수 있다.