【Domain】Open Compound Domain Adaptation
분류 : paperswithcode - Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
저자 : Ziwei Liu1∗, Zhongqi Miao2∗, Xingang Pan, Xiaohang Zhan
읽는 배경 : 판 페이 박사과정 선배가 추천해준 논문이자, 우상현 랩장과 박광영 박사과정 선배님이 최근에 발표하신 ‘Discover, Hallucinate, and Adapt’의 기본이 되는 논문이다.
읽으면서 생각할 포인트 : the present and problems and issues, ours Solution 흐름으로 정리하고 기록해놓자.
- 느낀점
- 이해 60%. 필요 논문을 찾아읽고 다시 읽어야 겠다.
- 다 읽은 후, 읽어야 겠다고 생각이 든 논문
- [45, 36, 28], Memory is storing class centroids.
- curriculum domain adaptation-y2018-c32 56 - curriculum domain adaptation에서 m이 의미하는것
- the domain-confusion loss-y2017,c1875 48 - Equ (1), (2)이 의미하는 수학적 의미 -> 이제 알았음.
- [27, 10], Adopting cosine classifiers, L2 norm before softmax classification.
- 10 -y2018c372
- t-SNE Visualization
- 이 논문에서 experiment compare하기 위해 사용했던 참고한 논문 자료.
- Digits: conventional unsupervised domain adaptation (ADDA [48], JAN [30], MCD [42])
- Digits: the recent multi-target domain adaptation methods (MTDA [9], BTDA [5], DADA [39])
- segmentation: three state-of-the-art methods, AdaptSeg [47], CBST [58], IBN-Net [35] and PyCDA [26]
논문 핵심
- Domain encoder를 만들어 내는 것. (Equation말고 Algorithm 2 figure 먼저 볼 것)
- 처음에는 Classification을 위한 class encoder와 같은 방식으로 학습시키다가,
Decoder( classEncoder(x), domainEncoder(x) ) = x이처럼 완벽한 reconstruction이 되게 만들면서,- classification 능력은 random label을 이용한 cross entropy loss로 제거해버린다.
- Domain encoder를 활용해서, target domain image feature와 source domain image feature 사이의 거리 계산하기
- Memory module(class centroids)을 사용해서, taget domain의 feature denoising 하기. (ProDA에서는 class centroids와의 거리 정보를 target domain feature에 곱해서 denoising 해줬지만…) 여기서는 V_transfer feature를 만드는 수식 사용했다.
- 자세한 내용은 코드를 보기. (논문보지 말고)
0. Abstract
- the present
- A typical domain adaptation approach이란?
- Clear distinctions between source and target
- Ours
- open compound domain adaptation (OCDA) 의 2가지 핵심기술
- instance-specific curriculum domain adaptation strategy : generalization across domains / in a data-driven self-organizing fashion(???)
- a memory module : the model’s agility(예민함, 민첩한 적응?) towards novel domains / memory augmented features for handling open domains. (메모리가, 우리가 가진 Feature Extractor 와 classifier 에 더 정확하게 작동하는, feature map이 생성되도록 도움을 준다.)
- 실험을 적용해본 challenges
- digit classification
- facial expression recognition
- semantic segmentation
- reinforcement learning
- open compound domain adaptation (OCDA) 의 2가지 핵심기술
1. Introduction
- the present & problem
- Supervised learning : 좋은 성능이지만 비현실적
- domain adaptation : 1 source : 1target 에 대해서 clear distinction를 정의하려고 노력하지만 이것도 비현실적. 현실은 많은 요소들(비,바람,눈,날씨)에 의해서 다양한 domain의 데이터가 함께 존재하므로.
- Ours - open compound domain adaptation
- more realistic
- adapt labeled source model /to unlabeled compound target
- 예를 들어 SVHN [33], MNIST [21], MNISTM [7], USPS [19], and SynNum [7] 는 모두 digits-recognition인데, 이들을 모두 다른 domain이라고 고려하는 것은 현실적이지 않다.
- 우리는 compound target domains로써 그들을 고려하고, unseen data까지 test해볼 계획이다.
- 기존의 domain adaptation : rely on some holistic measure of instance difficulty.
- 우리의 domain adaptation : rely on their individual gaps to the labeled source domain
- 네트워크 학습 과정
- classes in labeled source domain를 discriminate(classify) 하는 모델 학습
- (source와 많이 다르지 않은) easy target를 넣어서 domain invariance(domain의 변화에도 강건한)를 capture하게 한다.
- source와 easy target 모두에서 잘 동작하기 시작하면, hard target을 feed한다.
- 이런 방식으로 classification도 잘하고, 모든 domain에서 robust한 모델을 만든다.
- Technical insight
- Tech1 : domain-specific feature representations을 가지는 Classification Network에 대해서, source와의 feature distance가 가까운 target은 Network 변화에 많은 기여를 하지 않는 것을 이용한다. 그래서 distill(증류해 제거해나간다,) the domain-specific factors (즉 domain에 robust한 Network 제작)
- Tech2 : memory module이 inference를 하는 동안 open-domain에서도 정확한 feature를 추출하도록 도와준다. the input-activated memory features(input에 따라 다르게 행동하는 memory feature)
2. Relative work
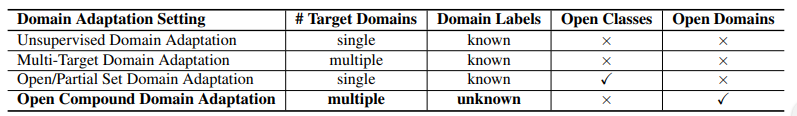
- Unsupervised Domain Adaptation :
- 1 source - 1 target
- cannot deal with more complicated scenarios
- 참고 논문들 : latent distribution alignment [12], backpropagation [7], gradient reversal [8], adversarial discrimination [48], joint maximum mean discrepancy [30], cycle consistency [17] and maximum classifier discrepancy [42].
- Latent & Multi-Target Domain Adaptation :
- clear domain distinction&labels(domain끼리의 차이가 분명함-하지만 현실은 continuous함) / not real-world scenario
- 참고 논문들 : latent [16, 51, 32] or multiple [11, 9, 54] or continuous [2, 13, 31, 50] target domains
- Open/Partial Set Domain Adaptation :
- target이 source에 없는 카테고리를 가지거나, subset of categories 를 가지거나.
- “openness” of domains = unseen domain data에 대해서 고려하기 시작
- 참고 논문들 : open set [37, 43] and partial set [55, 3] domain adaptation.
- Domain Generalized/Agnostic Learning :
- Learn domain-invariant universal representations (domain이 변하더라도 같은 특징을 잘 추출하는 신경망 모델)
- 참고 논문들 : Domain generalization [52, 23, 22] and domain agnostic learning [39, 5]
- 바로 위의 논문들의 문제점과 our 해결
- 문제점 : they largely neglect the latent structures inside the target domains
- 해결책 : Modelling the latent structures (figure4의 구조 같음) inside the compound target domain by learning domain-focused factors(domain_encoder)
3. Our Approach to OCDA
3.1. Disentangling Domain Characteristics with class labels in the source domain
Separate specific characteristics(representation) between classes.
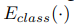 : classifier encoder up to the second-to-the-last layer
: classifier encoder up to the second-to-the-last layer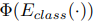 : the classifier
: the classifier
위의 Class_encoder로 발혀지지 않은 factors(features)들은 reflect domain characteristics.
 : domain encoder. 아래의 성질은 만족하게 encoder를 만들어 낸다.
: domain encoder. 아래의 성질은 만족하게 encoder를 만들어 낸다.Completeness : class[classifier ] encoder와 domain encoder의 정보를 모두 합쳐, decode하면 거의 완벽한 reconstruction이 된다. 즉 x에 대한 모든 factor(feature)를 가진다. (아래의 Algorithm2를 읽어보면 이해가능)
Orthogonality : E_domain(x) E_class(x)는 서로 상관관계가 없다.
이를 위해서 class-confusion algorithm 를 제안한다.
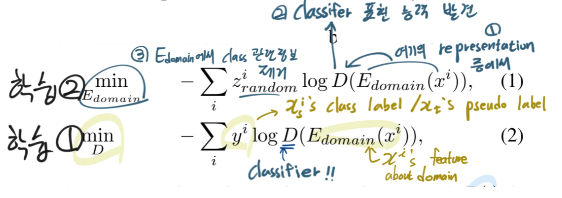
(1) 값이 최소가 되도록 domain encoder가 학습된다 (2) 값이 최소가 되도록 Discriminator가 학습된다 이 과정을 통해서, "Class_encoder라는 큰 수박에서, Domain_encoder의 능력을 가진 맛있는 부분을 살살살 긁어 뽑아내는 작업이다" 라고 생각하면 편하다. --- i : the instance index D : discriminator. - 이름은 discriminator인데 아래의 알고리즘을 잘보면, 저렇게 학습시키면 그냥 classifier가 된다.The E_domain(·) is class-confusing due to z^i_random
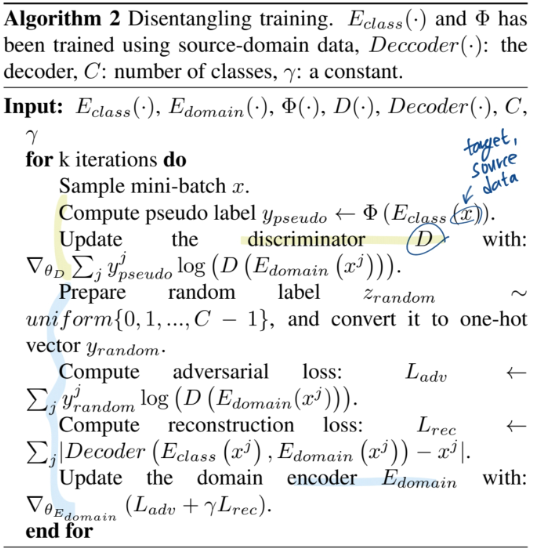
- 위의 알고리즘 과정을 통해서, Eecoder_domain은 class정보를 최대한 무시하면서도, domain에 관련된 representation만을 최대한 추출하는 Encoder가 되도록 학습된다.
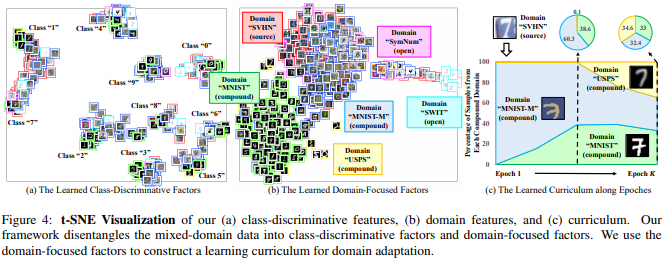
3.2. Curriculum Domain Adaptation
- target domain instance들을 source domain과의 거리를 기준으로 rank(정렬)한다.
- 거리를 측정하는 방법 :

- 가까운 domain instance들부터, Network 학습에 사용한다. 그때 Loss는 아래와 같다.
- Loss1 : One is the cross-entropy loss defined over the labeled source
- Loss2 : the domain-confusion loss[48]
3.3. Memory Module for Open Domains ⭐⭐
- 문제점 : target data를 기존의 신경망(classifier??)에 넣으면?? v_direct 나옴. v_direct 자체는 representation로써 불충분한 정보를 가지고 있다! 즉 신경망이 충분한 feature 추출 불가능!!
- 해결책 : Memory Module은 memory-transferred knowledge를 가지고 있다. 이것이 input으로 들어온 new domain data를 balance하게 만들어 준다.
- Class Memory (M)
- Store the class information from the source domain
- by [45, 36, 28], Store class centroids {c_k}(k = 1~K class number)
- Enhancer (v_enhance)

- 행렬곱 (1 x e) = (1 x d) * (d x e)
- M(d x e) 덕분에, target domain의 data가 source 쪽으로 이동한다.
- Domain Indicator (e_domain)
- 약간 learning Late 처럼, 얼마나 source 쪽으로 vector를 옮길 것인가. 를 말한다. 아래 수식 참조. gap이 크면 input vector를 크게 옮겨 놓고, gap이 작으면 input vector를 작게 옮긴다.
- Domain indicator =

- Source-Enhanced Representation (v_transfer)
- v_direct에서 source를 중심으로 balance가 맞춰진 vector
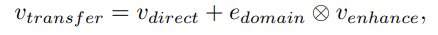
- ⊗ is element-wise multiplication
- Adopting cosine classifiers [27, 10], 이렇게 만들어지 v_transfer를 l2-normalize한다. 그리고 softmax classification layer에 보낸다.
- domain mismatch 에 효과적이다.
- v_direct에서 source를 중심으로 balance가 맞춰진 vector
- Class Memory (M)
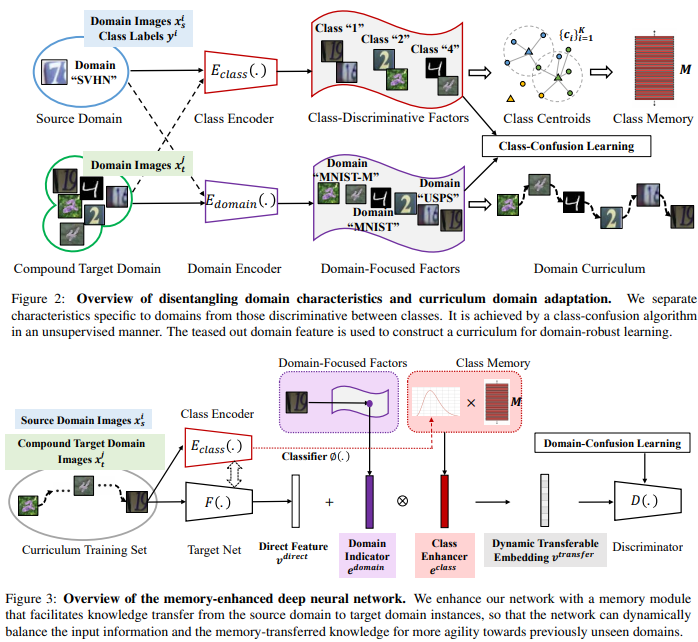
4. Experiments
Datasets
type source target open Classify-Digits SVHN MNIST, MNIST-M, and USPS SWIT C-Faces(Multi-PIE) C05 C08-C14 C19 C-Driving GTA-5 BDD100K BDD100K C-Mazes the GridWorld
Network Architectures
- backbone : LeNet-5, ResNet-18, VGG-16
- Compare with :
- Digits: conventional unsupervised domain adaptation (ADDA [48], JAN [30], MCD [42])
- Digits: the recent multi-target domain adaptation methods (MTDA [9], BTDA [5], DADA [39])
- segmentation: three state-of-the-art methods, AdaptSeg [47], CBST [58], IBN-Net [35] and PyCDA [26]
Ablation Study
- the Domain-Focused Factors Disentanglement - k-nearest neighbors
- the Curriculum Domain Adaptation - USPS is the furthest target domain -> Good Classification
- Memory-Enhanced Representations. - Figure 5
